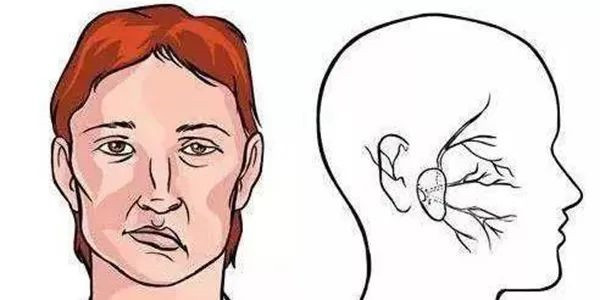
Hemifacialspasm (HFS) is a chronic progressive neuromuscular disease, which is characterized by irregular clonus and tonic contraction of the muscles in the unilateral facial nerve innervation area, more than emotional tension and fatigue, which can lead to serious mental disorders and psychological distress, affecting the quality of life of patients.
The main cause of HFS is vascular compression in the rootexitaone (REZ) area of the facial nerve. In rare cases, tumors and cerebrovascular diseases (such as intracranial aneurysms and intracranial arteriovenous malformations) have also been shown to be the cause of HFS.
However, the pathogenesis of HFS has not been determined. Some scholars believe that HFS is caused by a combination of mechanisms, including overexcited facial motor nuclei (central hypothesis), and demyelination or axonal injury (peripheral hypothesis) ³. microvascular decompression (MVD) has gradually become the standard treatment for HFS since Jannetta first introduced the procedure, which is designed to identify the responsible blood vessels and remove them from the facial nerve so as to relieve spasticity.
According to the report, efficient can reach more than 90% of MVD ⁴ - ⁵, but some patients with the treatment was invalid or easy to relapse, postoperative cranial nerve complication, even perioperative death.
Therefore, how to improve the efficiency of surgery and reduce complications is the target of clinical attention. With the development of neuroelectrophysiological monitoring technology, many medical centers began to apply these technologies to assist the implementation of MVD, and accumulated certain experience.
At the same time, the emergence of new monitoring technology also expands the idea of clinical application of this kind of technology. In this paper, the current clinical application of neuroelectrophysiological monitoring technology, Including the lateral diffusion reaction (lateralspreadresponse, LSR), Z - L reaction (ZLresponse ZLR), since the electromyography Figure (freerunningelectromyography frEMG), transcranial electrical stimulation motor evoked potential (transcranialelectricalmotorevokedpotentials TCeMEPs), blink reflex (blinkreflex, B R) and the application of facial F wave in HFSMVD are reviewed.